Health
The Most Compatible Solution to the Human Body from Turkish Scientists for Joint Pains Warned by The World Health Organization!
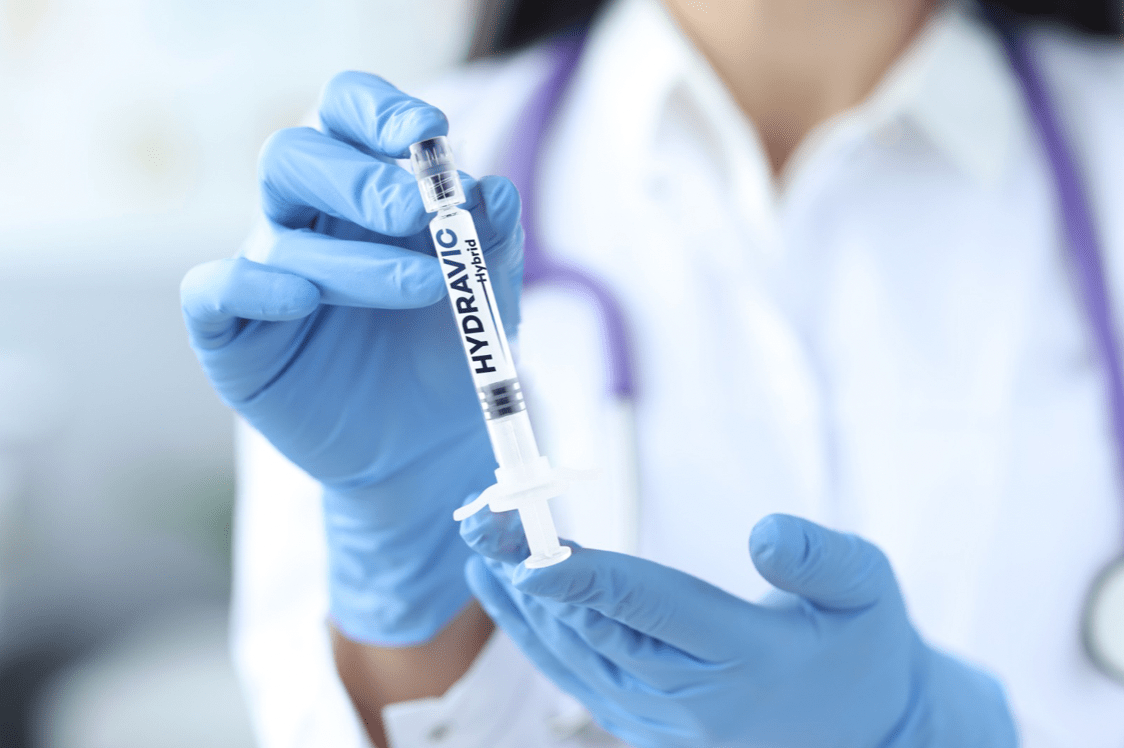
Degeneration of the joints significantly complicates daily life.
The World Health Organization (WHO) predicts that by 2050, 130 million people worldwide will suffer from joint pain and osteoarthritis. According to the World Health Organization, by 2050, 40 million people will lose function due to osteoarthritis.
The USA is the country with the highest prevalence of osteoarthritis in the world. More than half (18.7 million people) of adults with osteoarthritis in the United States are of working age (18-64 years). For this reason, osteoarthritis also causes a significant loss of workforce.
Against joint pain and osteoarthritis Scientists have made an important discovery. Developed with hybrid technology, HYDRAVIC received full marks from health authorities.
Developed with hybrid technology and minimizing the wear on cartilage, HYDRAVIC prevents patients from complaining of pain for up to 6-8 months. Turkish scientists who developed HYDRAVIC state that patient complaints will decrease significantly.
IMPORTANT INVENTION FROM SCIENTISTS
Against joint pain and osteoarthritis, which the world is looking for a cure for, scientists have made an innovative development in intra-articular fluids. Turkish scientists have developed an intra-articular injection with the most compatible gel form with the hybrid production technology. The product, which was launched under the HYDRAVIC brand, attracts great attention all over the world.
Developed with hybrid technology and minimizing the wear on cartilage, HYDRAVIC prevents patients from complaining of pain for up to 6-8 months. Turkish scientists who developed HYDRAVIC state that patient complaints will decrease significantly.
HYDRAVIC IS VERY CLOSE TO THE HYALURONIC ACID STRUCTURE IN THE BODY
HYDRAVIC, one of the first intra-articular injections with hybrid production technology in Turkey, stands out with its patient satisfaction. Stating that HYDRAVIC minimizes the wear on the cartilage and slows down the pressure created by the body on the cartilage, Prof. Dr. Serdar Sezer said, “HYDRAVIC was developed with inspiration from the complex structure of hyaluronic acid in the body. Patient satisfaction is quite good. Hybrid technology is a system that has been applied for the first time in Turkey, like its examples in the world. HYDRAVIC prevents patients from complaining of pain for up to 6-8 months.”
WHAT MAKES HYDRAVIC DIFFERENT IS THE DIFFERENCE OF ITS TECHNOLOGY!
Drawing attention to the importance of hybrid technology used in the production of HYDRAVIC, Professor Serdar Sezer “One of the features of hybrid technology is that it creates a triggering effect for the product to produce hyaluronic acid while being excreted from the body. This has been demonstrated in in-vitro and in-vivo experiments. Clinical long-term responses are very good. In our studies while developing these products, we have observed studies that have a longer duration of action with our innovative approach that repeats the results proven in the world. After its effectiveness has been proven, we are happy to introduce such a product to the market in the injection market, where we are one of the leading manufacturers in the field. We apply similar approaches across all our product models.” uses expressions.
Stating that they minimize the pain experienced by the patients during the injection, Professor Sezer said, “What makes HYDRAVIC different from other products is its technology. It is a product that does not make the patient feel very low or no pain during the injection and relieves the patient’s pain in a short time. In this technology, in addition to the molecular interaction, post-injection pain and swelling, etc., due to the production of the product in aseptic technical infrastructure. We minimize such complaints as possible.”
EUROPE’S LARGEST MEDICINE AND MEDICAL DEVICE R&D CENTER IS ESTABLISHED
Stating that Europe’s largest pharmaceutical and medical device R&D Center in the field of biomaterials was established in Turkey, Professor Sezer said, “To produce these kinds of products, the well-equipped infrastructures are required very serious costs. Many companies do not want to invest in such product groups, which have high infrastructure costs and are difficult to produce. With the new legislation, the costs increase significantly. We reach an annual capacity of 5.4 million units in 2023 in the HYDRAVIC production line, where we have achieved great success in the medical market.” he said.
Health
Dr. Teresa Tyson, DNP, Discusses The Hidden Healthcare Crisis in Remote Regions
Image source: Dr. Teresa Tyson, DNP, and Health Wagon
Access to healthcare remains a challenge for many individuals living in rural and remote areas, where medical facilities are scarce or difficult to reach. Many residents endure long travel times for even basic medical services, leading to delayed diagnoses and worsening health conditions. The lack of healthcare professionals further compounds the issue, leaving communities with inconsistent or inadequate care.
While technology and government initiatives have made strides in addressing these disparities, Dr. Teresa Tyson, DNP, notes how there are many obstacles still hindering widespread improvement. Bridging the healthcare gap requires a combination of innovative solutions, infrastructure development, and policy changes to ensure that medical services reach those who need them most.
Limited Access to Medical Care
Many remote regions struggle with a severe lack of healthcare facilities, leaving residents with minimal options for medical treatment. Hospitals and clinics are often located hours away, making even routine checkups a logistical challenge.
A shortage of medical professionals further worsens the situation, as many doctors and nurses prefer to work in urban areas with better resources and career opportunities. As a result, rural communities often rely on understaffed clinics or visiting healthcare workers who may not be available consistently. This leads to delayed diagnoses and inadequate treatment for chronic conditions. Many rural clinics operate with limited medical supplies, making it difficult to provide comprehensive care even when healthcare professionals are available.
In some cases, patients must travel long distances just to receive basic care, often at great personal and financial costs. The burden of transportation, time off work, and the uncertainty of available treatment discourage many from seeking medical attention until their conditions become severe.
Health Risks and Consequences
Delays in medical care often mean that conditions that could have been treated early turn into serious health complications. Many individuals in remote areas develop chronic illnesses that go undiagnosed for years simply because healthcare services are too far away or difficult to access. Diseases that are manageable with regular monitoring, such as diabetes or hypertension, frequently spiral out of control due to the lack of consistent medical supervision.
Beyond physical health, the absence of adequate healthcare also takes a toll on mental well-being. Isolation and limited access to mental health professionals leave many struggling with anxiety, depression, and other psychological conditions without proper support. In small, tight-knit communities, stigma around mental health can make it even harder for individuals to seek help, further exacerbating the crisis.
Preventable diseases continue to spread in these areas due to the lack of vaccinations, screenings, and early interventions. Without proper healthcare infrastructure, outbreaks of common illnesses can have devastating effects, particularly on children and the elderly. The combination of poor access, financial barriers, and limited awareness creates a cycle where minor health concerns escalate into life-threatening conditions.
Challenges in Expanding Healthcare Services
Building and maintaining healthcare infrastructure in remote regions comes with considerable hurdles. Poor road conditions and unreliable transportation make it difficult for medical professionals to reach patients, and in some cases, ambulances are unavailable, forcing residents to rely on personal vehicles or community efforts to transport those in need. In areas with extreme weather conditions, seasonal challenges further complicate healthcare delivery, cutting off entire communities during certain times of the year. These conditions make it nearly impossible for emergency medical teams to provide timely assistance in critical situations.
Funding remains a major obstacle, as rural healthcare facilities often struggle with limited financial resources. Many small clinics operate on tight budgets, lacking essential medical equipment and supplies. Without sufficient investments, these facilities cannot expand their services, making it harder to attract and retain qualified healthcare workers. As a result, many professionals opt to work in urban settings where they have access to better salaries, career advancement, and modern medical technology.
Role of Technology in Bridging the Gap
Advancements in technology are offering new ways to connect patients in remote areas with medical professionals. Telemedicine has made it possible for individuals to consult doctors without having to travel long distances, reducing delays in diagnoses and treatment. Virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and mobile health apps allow patients to receive medical advice without needing to visit overcrowded or distant healthcare facilities. In addition to telemedicine, artificial intelligence is being used to assist in diagnosing conditions remotely, helping bridge the gap in specialist care.
Despite its potential, implementing technology-driven healthcare solutions in rural regions is not without obstacles. Many areas lack reliable internet access or the necessary digital literacy to make full use of telehealth services. Even when technology is available, the cost of devices and connectivity can create another barrier, preventing low-income households from benefiting fully. Addressing these issues requires a combination of infrastructure development, education, and financial support to ensure that technology can be effectively integrated into rural healthcare systems.
Efforts to Improve Rural Healthcare
Governments and nonprofit organizations are actively working to address the healthcare challenges faced by remote communities. Investment in medical outreach programs, mobile clinics, and training initiatives for local healthcare workers has helped bring essential services to those who need them most. Some regions have introduced incentive programs to encourage doctors and nurses to work in underserved areas, offering student loan forgiveness, housing assistance, or higher salaries.
Community-led initiatives also play a crucial role in improving healthcare access. Local volunteers and advocacy groups often step in to provide educational workshops, vaccination drives, and wellness programs tailored to the specific needs of their communities. These grassroots efforts help bridge gaps where formal healthcare systems fall short, ensuring that residents receive at least some level of medical support.
Future Prospects for Remote Healthcare
Innovations in medical technology, policy changes, and raising awareness are shaping the future of rural healthcare. The expansion of telehealth services, combined with improved infrastructure, has the potential to make healthcare more accessible and efficient. Continued investment in mobile medical units and community-based programs could ensure that even the most isolated areas receive the care they need. Research into low-cost, portable medical devices is also opening new doors for remote diagnostics and treatment.
Sustained progress will depend on collaboration between governments, healthcare providers, and local communities. Long-term solutions require more than temporary programs; they demand systemic changes that prioritize equitable medical access. If these efforts continue to grow, rural healthcare systems may finally move toward lasting improvements that benefit future generations.
-

 Tech4 years ago
Tech4 years agoEffuel Reviews (2021) – Effuel ECO OBD2 Saves Fuel, and Reduce Gas Cost? Effuel Customer Reviews
-

 Tech6 years ago
Tech6 years agoBosch Power Tools India Launches ‘Cordless Matlab Bosch’ Campaign to Demonstrate the Power of Cordless
-

 Lifestyle6 years ago
Lifestyle6 years agoCatholic Cases App brings Church’s Moral Teachings to Androids and iPhones
-

 Lifestyle4 years ago
Lifestyle4 years agoEast Side Hype x Billionaire Boys Club. Hottest New Streetwear Releases in Utah.
-

 Tech6 years ago
Tech6 years agoCloud Buyers & Investors to Profit in the Future
-

 Lifestyle5 years ago
Lifestyle5 years agoThe Midas of Cosmetic Dermatology: Dr. Simon Ourian
-

 Health6 years ago
Health6 years agoCBDistillery Review: Is it a scam?
-

 Entertainment6 years ago
Entertainment6 years agoAvengers Endgame now Available on 123Movies for Download & Streaming for Free
